Will AI replace search engines?
The short answer is, no—AI will not replace search engines completely, but it’s already changing how we search.
Search is no longer just about getting a list of websites. People want clear, direct answers without having to click through multiple links.
Of course, people still use Google to search for things. But now, you can also incorporate AI search engines like ChatGPT for in-depth or specific query answers, such as why your dog is acting weird, or how to format your resume in a tone-perfect single paragraph.
This subtle switch is exactly what’s shaking up the future of search.
Why people are turning to AI for answers
People are turning to AI search engines for answers because they save time, reduce clutter, and deliver direct, personalized responses in natural language—something traditional search engines often fail to do.
This explains why Google’s organic CTRs fell sharply, from 1.41% to 0.64% year-over-year, for results where AI Overviews were present.
Google co-founder Sergey Brin recently explained that AI is changing search from just pulling up links to actually doing the research for you. Instead, AI now scans thousands of results, connecting the dots, and producing a clear answer in seconds. What used to take a person hours or even days to figure out, AI can now do in a single response.
In fact, new data already reveals a dramatic change in online search behavior:
So why the sudden shift to AI-powered search? The short answer is that traditional search engines give you too many options. AI gives you one clear answer, and that’s what users are shifting toward.
Here’s a more detailed explanation:
- Traditional search is cluttered: Search engines are overloaded with ads, SEO-bloated articles, and outdated content. Users don’t want to click 7 links to find one answer. AI skips that step.
- AI gives instant answers: Instead of scanning pages, AI generates clear, summarized responses in seconds. It answers like a person would, based on what you’re actually asking.
- AI feels more personal: The response style, tone, and context adjust based on how you phrase your query, so it feels like a conversation.
💡Also learn about: Google AI Mode and How It Affects Your Traffic
The evolution of search engines: From directories to dominance
Search engines have evolved from manually curated link directories to AI-enhanced systems capable of understanding human language and intent, but their purpose remains the same: to help users find answers.
When search engines were first introduced, users searched for websites. Today, we search for ideas, problems, and outcomes. That shift in search intent is what made traditional search so ripe for disruption by AI.
The first era: directories and basic keyword matching
In the 1990s, search was static and manual. Yahoo! Directory, for example, didn’t “search” in the modern sense. They grouped websites by categories—like a digital phone book. Discovery was limited to what human editors added, and relevance was subjective.
Then came keyword-based engines like AltaVista and WebCrawler, which crawled the open web and indexed content. But they lacked a meaningful way to determine which results were useful.
There was no trust layer. Every result was weighted equally, and spam was a common occurrence.
The second era: link-based authority and Google’s rise
Google’s PageRank model, introduced in 1998, contributed significantly to the rise and expansion of the search engine giant as we know it today. This model treated links as votes of confidence. The more reputable pages that link to you, the more credible your content appears to be.
This was the foundation of modern search relevance and led to the emergence of the SEO practices we recognize today.
By the early 2000s, Google had pulled ahead because it offered:
- Relevance based on link structure
- A clean, fast interface
- Scalable crawling and indexing infrastructure
As a result, by 2004, Google was processing over 200 million queries per day—a number that has now grown to the trillions per year.
The third era: personalization and contextual search
As user data became more accessible, search evolved from one-size-fits-all to tailored results. Google began factoring in:
- Search history
- Location
- Device type
- Real-time trends
Then came the Knowledge Graph (2012), which marked the first attempt to go beyond links and understand relationships between entities. This means you could search for “Tom Hanks movies” and get a carousel, not just blog links.
Or, you can search for “Mona Lisa” and receive search results related to Leonardo da Vinci, the Louvre Museum, and so on.

This algorithm change also marked a turning point: users began expecting answers from search engines like Google, not just plain results, such as blue links.
The fourth era: machine learning enters search (RankBrain, BERT, MUM)
Between 2015 and 2021, machine learning transformed Google search from word matching to meaning matching. This era marked Google’s shift from algorithmic ranking to actual language understanding.
These are the major AI systems running in Google search, along with their functions:
- RankBrain (2015): This is a machine learning system that helps Google understand what you mean when your search is unclear or unusual. It examines the full query, identifies patterns in past searches, and determines the types of results people clicked on.
- Example: If you search “best laptop with fast charging,” RankBrain knows you’re looking for reviews, not just definitions of “fast charging.”
- Neural Matching (2018): This helps Google connect what you’re searching for with ideas and terms that might not use the same words. It’s like Google learning to understand synonyms and concepts.
- BERT (2019): BERT helps Google understand the meaning of words based on the whole sentence. It’s especially good with longer, more natural-sounding questions.
- Example: For example, when you search “Can you get medicine for someone else at a pharmacy?” — BERT understands “for someone else” is the key part, not just “medicine” and “pharmacy.”
- MUM (2021): Multitask Unified Model is trained to understand text, images, and even different languages. It’s built to answer complex questions that don’t have one obvious answer.
Together, these models laid the groundwork for generative AI in search, where engines don’t just find answers, they form them.
The fifth era: the shift from retrieval to generation
AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s own Search Generative Experience, or AI Overviews, represent a structural shift. Instead of showing 10 web page options in SERPs, this form of search generates a direct answer based on a deep scan of web content.
For instance, a query like “compare M1 vs M2 MacBooks for video editing” yields a summarized comparison, saving users the effort of sifting through numerous articles or review videos.
As a result, user preferences are aligning with this shift, as 71.5% report using AI tools for search.
So, what changed?
Search engines no longer just index web pages—they understand, predict, and respond to user queries.
This progression—from directories to intent-based retrieval to generative response—is why AI isn’t replacing search. The future of search engines is being impacted by how people interact with them.
And that changes everything for users, content creators, and marketers alike.
💡 Learn more about: How to Measure SEO Success in Times of AI Search
Will AI disrupt Google search or reshape it?
AI will not replace search engines like Google, but it will fundamentally reshape how, where, and why people search. Traditional engines like Google will remain essential, but the experience of “searching” is no longer tied to a single box on a webpage.
As a result, we’re entering the era of “search everywhere optimization.” This means users will ask questions in chatbots, get recommendations from social feeds, and use voice interfaces to access information on the go.
In short, the point of search entry has changed, and so have the expectations: users don’t just want links—they want complete, contextual answers wherever they are.
As a result, marketers need to think beyond traditional search engine optimization by optimizing for other platforms, such as AI search, social media platforms, YouTube, community forums like Reddit, review sites, and more.
Here’s how this shift is reshaping the current search landscape, not disrupting it:
1. The rise of hybrid search experiences
Hybrid search, which blends traditional web indexing with generative AI outputs, is already becoming the default. For example, Google’s AI Overviews is the clearest sign. When you search for a query on Google, you now see:
- An AI-generated summary
- Follow-up questions through “People Also Ask” boxes
- Traditional links and knowledge panels
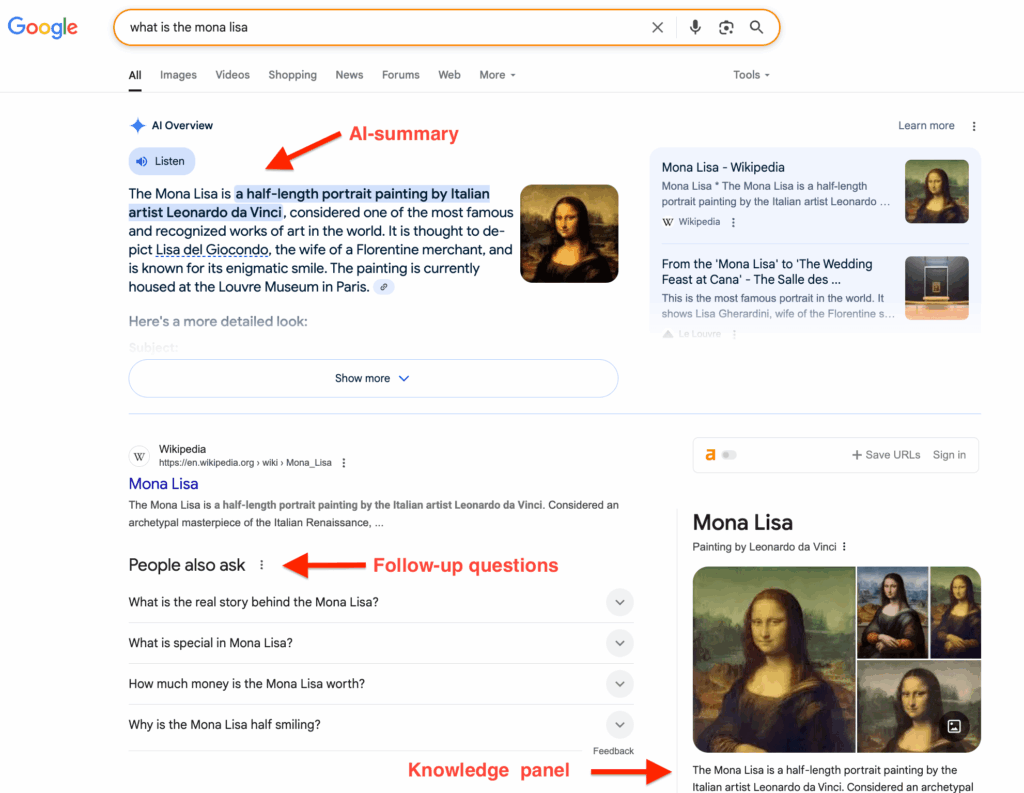
Even Bing, through its integration with GPT-4, is following this hybrid approach. Users can ask a question in Bing Chat, receive an AI-generated answer, and then click through to the sources immediately.
Meanwhile, tools like Perplexity provide real-time citations with summaries, allowing users to validate AI outputs on the spot.
This hybrid model addresses two needs at once:
- Users get instant summaries
- They still have access to sources and depth
2. User behavior trends and generational shifts
How users search is now deeply influenced by age, device, and expectation.
- Gen Z and Gen Alpha don’t “Google” everything. They ask ChatGPT, search on TikTok, or get recommendations from YouTube. In fact, eMarketer reports that Gen Z is 25% less likely to use Google for searches compared to Gen X, and 46% favor social media over traditional search engines.
- Millennials use a mix: Google for factual search, ChatGPT for summaries, and Reddit for decision-making.
- Older generations (Gen X and Boomers) still trust traditional search engines most, but even here, tools like Gemini and Copilot are gaining ground, especially for tasks like trip planning, health research, and product reviews.
Behavior is shifting from “searching” to “asking”—and from clicking to scanning summaries. This change is accelerating as AI models improve at understanding intent and tone.
This shift in search habits also means marketers need to evolve and modernize their existing SEO practices to boost their visibility.
3. Emergence of various search platforms (AI search, social media, YouTube, etc)
Search is now fragmented, and that’s not a bad thing. Users no longer rely on a single platform. Instead, they choose based on intent.
For instance:
- YouTube is the world’s second-largest search engine, processing over 3 billion daily searches, primarily for tutorials, reviews, and explainers.
- TikTok is being used to influence purchasing decisions and as a product discovery platform for a large number of Gen Z users, according to Search Engine Land.
- Reddit has become a major source of trusted peer recommendations, with 72% of tech users using the platform for reviews and 43% of U.S users using it as a source of news.
| Intent | Platform |
| Direct answer or quick summarization | ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude |
| How-to or visual guide | YouTube, Instagram, Pinterest |
| Peer opinions or real use cases | Reddit, TikTok |
| Shopping, product comparisons | Amazon, Google Shopping, Bing Chat |
| Job-related searches | LinkedIn, niche platforms like AngelList |
But this fragmentation in tools and platforms isn’t the death of search—it’s the distribution of search intent.
Search habits are now integrated into AI chatbots, apps, feeds, car dashboards, wearables, and browsers. This means marketers and content creators have to optimize for discoverability everywhere, not just on Google.
Key takeaway: Search engines won’t disappear. But the monopoly on where and how we search is breaking. The future isn’t about replacing Google—it’s about recognizing that search is happening across platforms, in multiple formats, and often without a search bar at all.
This is why traditional SEO must evolve into search everywhere optimization. This strategy ensures that your content can be found, understood, and accurately summarized by both human users and AI systems across various platforms.
💡 Related to your reading: Will AI Replace SEO?
What this means for marketers, SEO, and content creators
The bottom line is: Search engines aren’t going anywhere, but users now have more ways to search. From AI tools like ChatGPT to platforms like YouTube and Reddit, search is no longer limited to Google.
This shift demands a new strategy: search everywhere optimization. To stay relevant, marketers must optimize content across AI, social, and niche platforms—not just traditional search engines.

Here’s how content creators and marketers can achieve this:
1. Shifting focus from SEO to AIO: Adapting to AI-driven search
The traditional SEO model, centered on optimizing content for search engine algorithms, is evolving into Artificial Intelligence Optimization (AIO) or Generative Engine Optimization (GEO).
This shift acknowledges how AI tools, such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI summaries, are increasingly influencing how users discover information.
GEO focuses on creating content that AI systems can easily find, understand, and reference. This involves structuring content with clear headings, concise language, and contextually rich information that aligns with user intent.
2. Prioritize original, valuable content in the AI era
In an age where AI can generate content rapidly, originality and depth have become paramount. AI systems tend to favor content that demonstrates Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
This means that content creators must focus on producing material that offers unique insights, backed by credible sources and real-world experience.
A blog post from Google states that focusing on unique, valuable content for readers is a significant factor that helps you rank for AI Overviews.
John Mueller has also expressed, “Even the best content can be disappointing to people if they arrive at a page that’s cluttered, difficult to navigate, or makes it hard to find the main information they’re seeking. Ensure that you’re providing a good page experience for those who arrive either from classic or AI search results.”
3. Evolving for “search everywhere optimization”
The concept of search everywhere optimization (SEO 2.0) recognizes that users are seeking information across a multitude of platforms, not just traditional search engines. This includes social media, video platforms, forums, and AI chatbots.
To adapt to this new future of search engines and SEO, marketers should:
- Diversify content distribution: Share content across various platforms like YouTube, TikTok, LinkedIn, and Reddit to reach different audience segments.
- Optimize for platform-specific algorithms: Understand and implement best practices for each platform’s search and recommendation systems. For example, social media platforms may be effective for brand awareness, while YouTube and Reddit can be more suitable for bottom-of-the-funnel marketing activities.
- Leverage structured data: Utilize schema markup to assist AI and search engine algorithms in understanding and presenting your content effectively.
- Engage with communities: Participate in forums and social media discussions to build authority and trust. Collaborate with industry experts to get your brand mentioned in more high-authority websites.
Future-proof your AI visibility strategy with Writesonic
Search isn’t just happening on Google anymore. Your customers are asking ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini. The question is: are they seeing your brand?
Writesonic’s Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) tool helps you track and improve your visibility across all major AI search platforms.
From ChatGPT responses to Google’s AI Overviews, GEO by Writesonic shows exactly how your brand is mentioned, how you rank against competitors, and what AI platforms are citing about you.
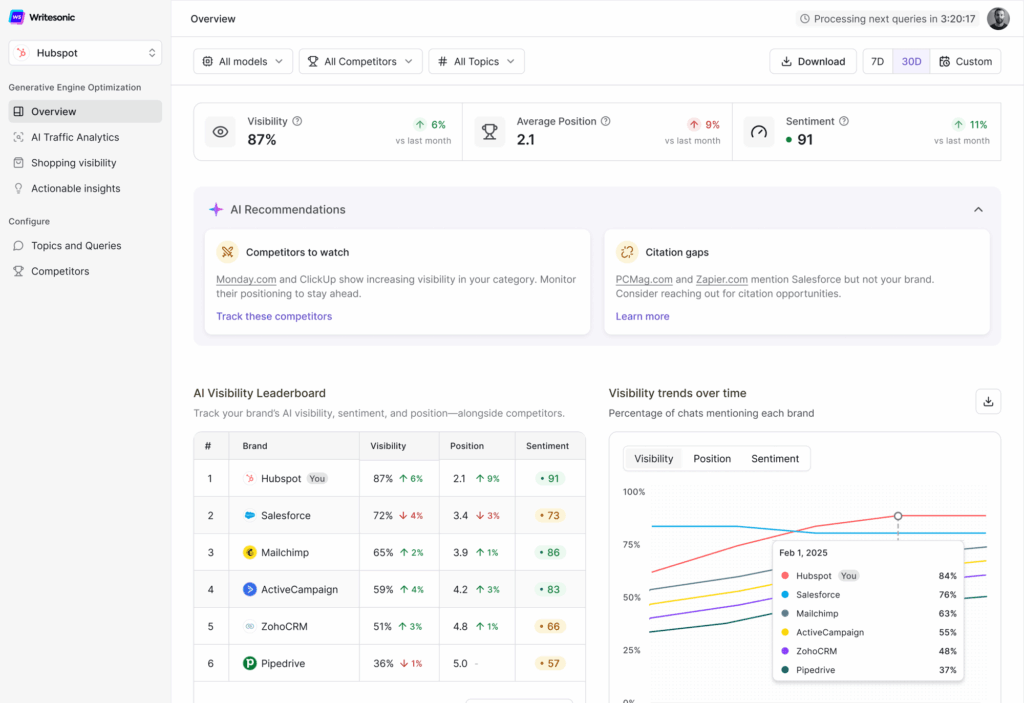
Get real data—like which pages AI models access most, what tone they use when describing your brand, and where you’re missing out on mentions others are getting.
Here’s what you’ll get with Writesonic’s AI Traffic Analytics:
- Your brand’s AI visibility percentage, sentiment score, and ranking position.
- A clear view of which prompts and topics your brand shows up in.
- Real-time insights into which platforms mention you, and how often.
- Competitor benchmarking across visibility, sentiment, and share of voice.
This isn’t just traditional SEO. It’s a new frontier—AI search visibility—and the brands that adapt early will dominate.
Take control of how AI sees your brand before your competitors do.


















